
I am a third-year Ph.D. student at Beijing Jiaotong University, advised by Prof. Wenjia Niu in Department of Information Security, School of Computer Science and Information Technology. I have been visiting Deakin University (working with Prof. Gang Li ) from Nov, 2024 to Mar, 2025.
I obtained my bachelor degree at Beijing Information Science & Technology University in 2020. And, I fortunately have been visiting Tsinghua University (co-advised by Prof. Juanzi Li and Dr. Peng Zhang) from Nov, 2018 to June, 2020. During my time at Tsinghua, I completed my undergraduate thesis "Research on News Entity Open Relation Extraction", awarded Excellent Undergraduate Thesis of Beijing.
My research interests lie in (1) AI security including adversarial attack, backdoor attack, and privacy attack on AI systems; (2) Explainable AI to enhance the transparency and trustworthiness of AI systems; (3) Brain-inspired computing with a focus on applications of spiking neural networks in AI systems. Here is my CV .
Email: tianyunzhe {at} bjtu [dot] edu [dot] cn
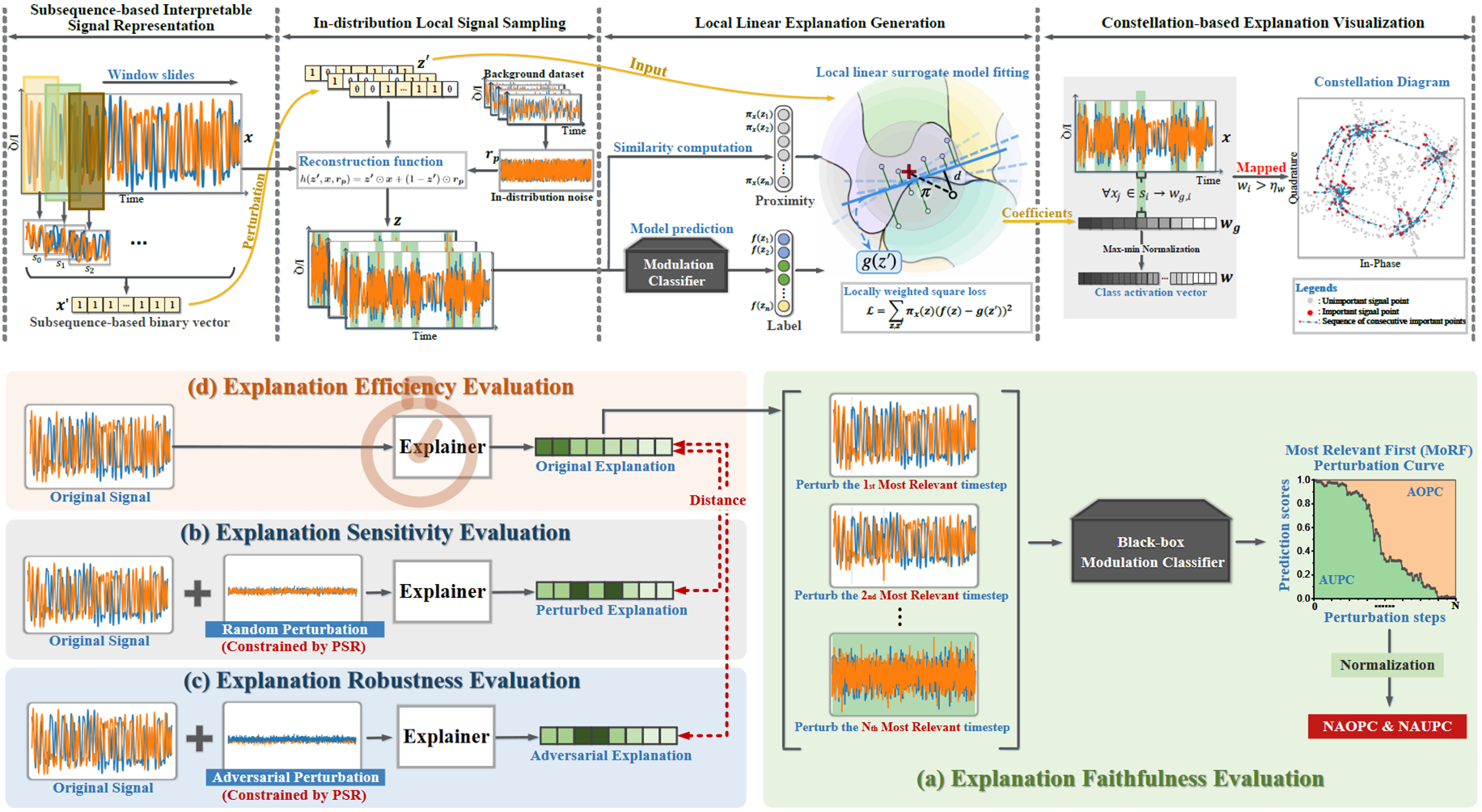
Recent advances in deep learning (DL) have brought tremendous gains in signal modulation classification. However, DL-based classifiers lack transparency and interpretability, which raises concern about model's reliability and hinders the wide deployment in real-word applications. While explainable methods have recently emerged, little has been done to explain the DL-based signal modulation classifiers.
In this work (Tian et al, TR'24), we propose a novel model-agnostic explainer, Model-Agnostic Signal modulation classification Explainer (MASE), which provides explanations for the predictions of black-box modulation classifiers. With the subsequence-based signal interpretable representation and in-distribution local signal sampling, MASE learns a local linear surrogate model to derive a class activation vector, which assigns importance values to the timesteps of signal instance. Besides, the constellation-based explanation visualization is adopted to spotlight the important signal features relevant to model prediction. We furthermore propose the first generic quantitative explanation evaluation framework for signal modulation classification to automatically measure the faithfulness, sensitivity, robustness, and efficiency of explanations. Extensive experiments are conducted on two real-world datasets with four black-box signal modulation classifiers. The quantitative results indicate MASE outperforms two state-of-the-art methods with 44.7% improvement in faithfulness, 30.6% improvement in robustness, and 44.1% decrease in sensitivity. Through qualitative visualizations, we further demonstrate the explanations of MASE are more human interpretable and provide better understanding into the reliability of black-box model decisions.
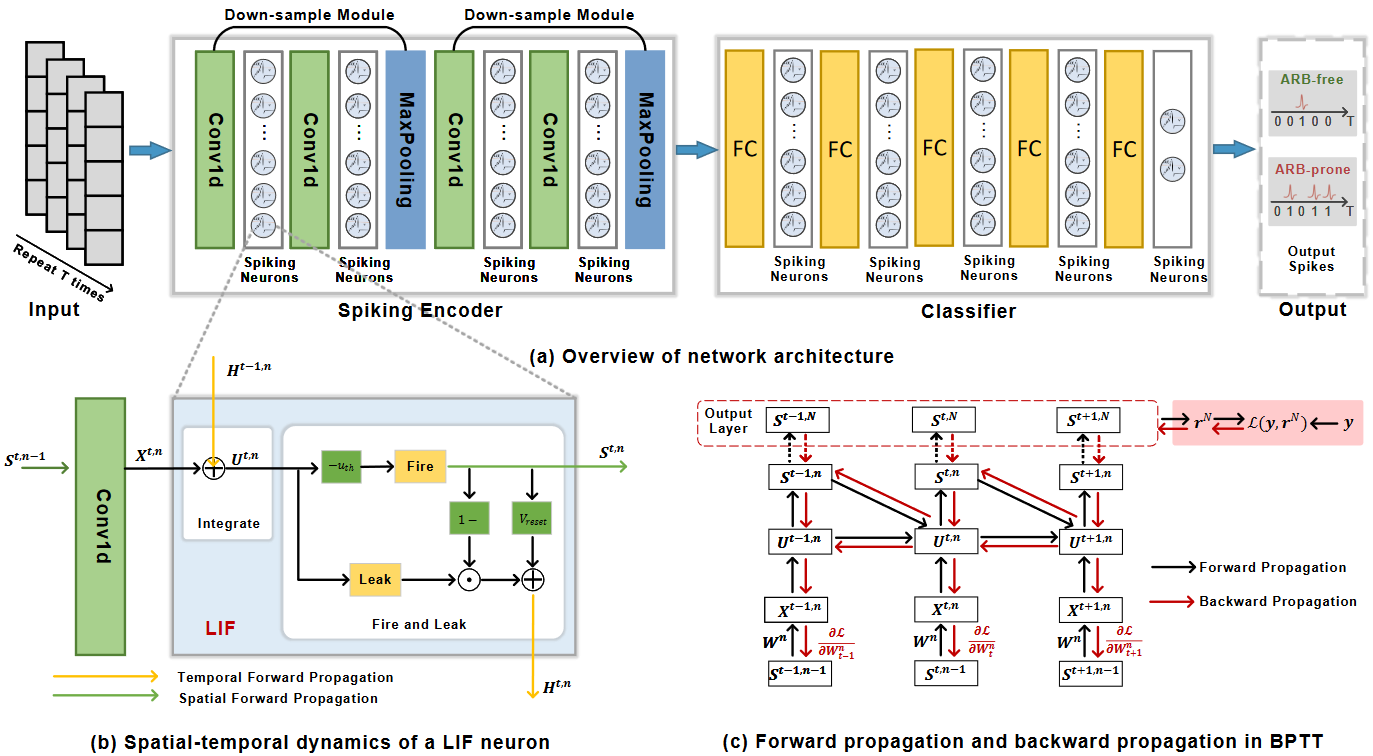
To alleviate the impact of software aging, primarily induced by aging-related bugs (ARBs), ARB prediction has drawn considerable interest from both academia and industry. Recent advances in deep learning (DL) have brought tremendous gains in ARB prediction. However, due to the limited size and extreme class imbalance in ARB datasets, conventional artificial neural networks (ANNs) are susceptible to overfitting, resulting in a suboptimal generalization performance.
In this paper (Tian et al, ISSREW'23), we take advantage of sparse and binary nature of spiking communication in spiking neural networks (SNNs), which inherently provides a brain-inspired regularization to effectively alleviate overfitting. We propose the first spiking convolutional neural network-based ARB prediction model (ARB-SCNN), comprising a spiking encoder followed by a classifier and utilizing the Leaky Integrate-and-Fire neuron as the basic spiking computing unit. Considering the spatial-temporal dynamics and the non-differentiability nature, we develop a dedicated training framework for ARB-SCNN, which incorporates the rate coding-based mean square error (MSE) loss and employs the backpropagation through time with the surrogate gradient. Finally, extensive experiments on two real-world ARB datasets demonstrate that our ARB-SCNN effectively mitigates overfitting, improving generalization performance by 7.82% compared to the state-of-the-art DL-based classifiers, and it exhibits up to 5× better computational energy efficiency.
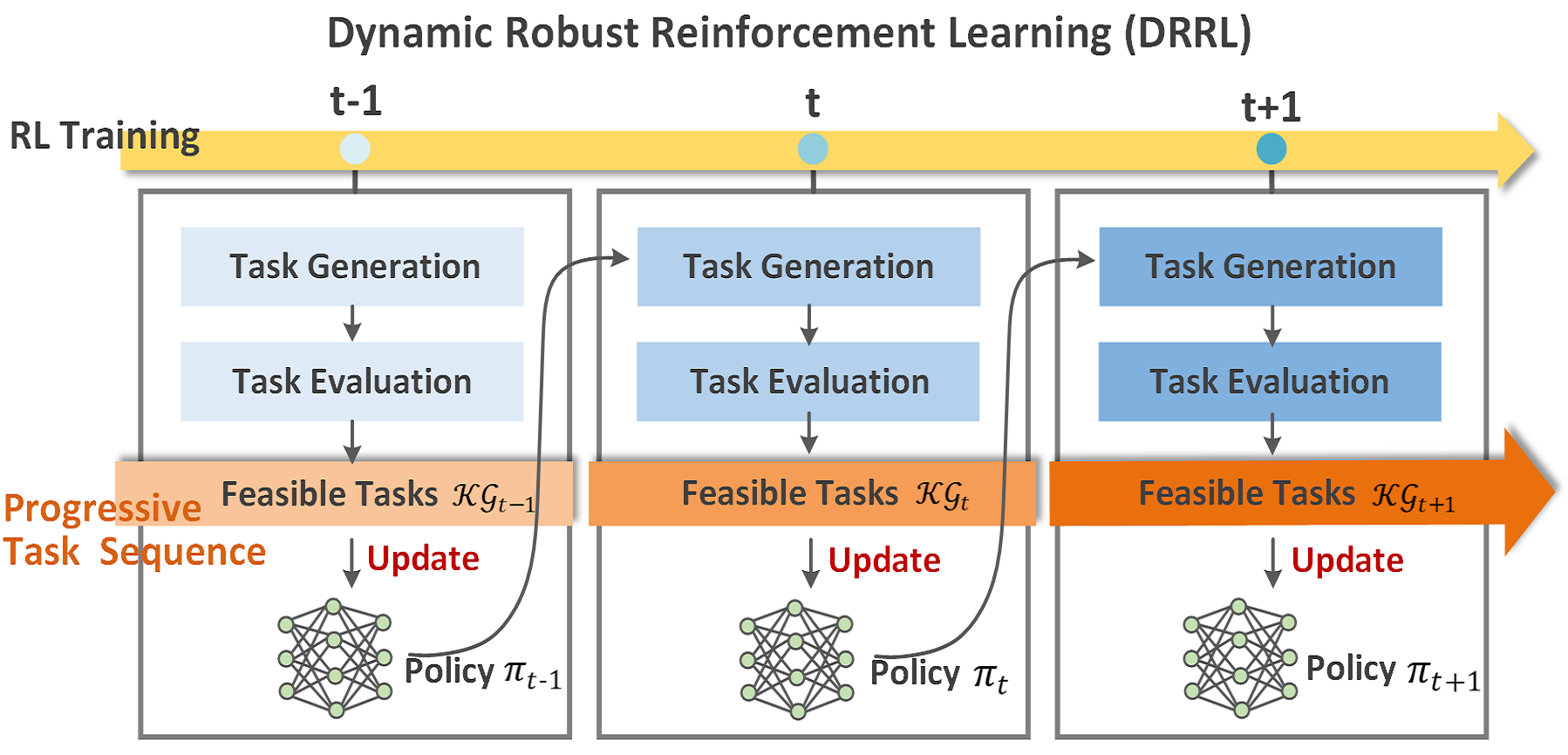
Robust reinforcement learning (RL) has been a challenging problem in reliable aspects due to the gap between laboratory simulation and real world. Existing efforts typically address the robust RL problem by solving a maxmin problem, which maximizes the cumulative reward under the worst-possible perturbations. However, the worst-case formulation either leads to overly conservative solutions or unstable training process, which further affects the policy robustness.
Motivated by this, in our recent work (Li et al, IJCAI'23), we tackle this problem from both formulation definition and algorithm design. First, we formulate the robust RL as a max-expectation optimization problem, where the goal is to an optimal policy under both the worst cases and the non-worst cases. Then, we propose a novel framework DRRL to solve this max-expectation optimization problem, in which a task generation and sequencing mechanism is introduced to iteratively output new tasks at the appropriate level of difficulty for the current policy. With these progressive tasks, we realize multi-task learning to improve policy robustness and training stability. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DRRL exhibits significant performance on the unmanned CarRacing game and multiple high-dimensional MuJoCo environments.
Yunzhe Tian, Yike Li, Kang Chen, Zhenguo Zhang, Endong Tong,
Jiqiang Liu, Fangyun Qin, Zheng Zheng, and Wenjia Niu.
Towards Label-Efficient Deep Learning-based Aging-related Bug Prediction with Spiking Convolutional Neural Networks. In IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computing, 2025.
Yunzhe Tian, Dongyue Xu, Endong Tong, Rui Sun, Kang Chen, Yike Li, Thar Baker, Wenjia Niu, and Jiqiang Liu. Toward Learning Model-Agnostic Explanations for Deep Learning-Based Signal Modulation Classifiers. In IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2024.
Yunzhe Tian, Yike Li, Kang Chen, Endong Tong, Wenjia Niu, Jiqiang Liu, Fangyun Qin, Zheng Zheng. Mitigating Overfitting for Deep Learning-based Aging-related Bug Prediction via Brain-inspired Regularization in Spiking Neural Networks. In The IEEE 34th International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering Workshops (ISSREW 2023), 2023.
Yike Li, Yunzhe Tian (co-first author), Endong Tong, Wenjia Niu, and Jiqiang Liu. Robust Reinforcement Learning via Progressive Task Sequence. In The Proceedings of the 32nd International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI 2023), 2023.
Yunzhe Tian, Yike Li, Yingxiao Xiang, Wenjia Niu, Endong Tong, and Jiqiang Liu. Curricular Reinforcement Learning for Robust Policy in Unmanned CarRacing Game. In NDSS 2021, Workshop on Automotive and Autonomous Vehicle Security (AutoSec).
Yunzhe Tian, Jiqiang Liu, Endong Tong, Wenjia Niu, Liang Chang, Qi Alfred Chen, Gang Li, and Wei Wang. Towards Revealing Parallel Adversarial Attack on Politician Socialnet of Graph Structure. In Security and Communication Networks (SCN), 2021 .
Yunzhe Tian, Yingdi Wang, Endong Tong, Wenjia Niu, Liang Chang, Qi Alfred Chen, Gang Li, and Jiqiang Liu. Exploring Data Correlation between Feature Pairs for Generating Constraint-based Adversarial Examples. In The IEEE 26th International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems (ICPADS 2020), 2020.
徐冬月, 田蕴哲, 陈康, 李轶珂, 吴亚伦, 童恩栋, 牛温佳, 刘吉强, 史忠植. 面向信号调制识别的对抗攻击与防御综述. 计算机研究与发展, 2024.
Jiayin Song, Yike Li, Yunzhe Tian, Xingyu Wu, Qiong Li, Endong Tong, Wenjia Niu, Zhenguo Zhang, and Jiqiang Li.
Knowledge-Driven Backdoor Removal in Deep Neural Networks via Reinforcement Learning.
In The 17th International Conference on Knowledge Science, Engineering and Management (KSEM 2024), 2024.
Yalun Wu, Yingxiao Xiang, Endong Tong, Yuqi Ye, Zhibo Cui, Yunzhe Tian, Lejun Zhang, Jiqiang Liu, Zhen Han, and Wenjia Niu.
Improving the Robustness of Pedestrian Detection in Autonomous Driving With Generative Data Augmentation.
In IEEE Network, 2024.
Yike Li, Wenjia Niu, Yunzhe Tian, Tong Chen, Zhiqiang Xie, Yalun Wu, Yingxiao Xiang, Endong Tong, Thar Baker, and Jiqiang Liu. Multiagent Reinforcement Learning-Based Signal Planning for Resisting Congestion Attack in Green Transportation. In IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking (TGCN), 2022.
Endong Tong, Wenjia Niu, Yunzhe Tian, Jiqiang Liu, Thar Baker, Sandeep Verma, and Zheli Liu. A Hierarchical Energy-efficient Service Selection Approach with Qos Constraints for Internet of Things. In IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking (TGCN), 2021.
Yike Li, Yunzhe Tian, Endong Tong, Wenjia Niu, Yingxiao Xiang, Tong Chen, Yalun Wu and Jiqiang Liu. Curricular Robust Reinforcement Learning via GAN-based Perturbation through Continuously-scheduled Task Sequence. In TSINGHUA Science and Technology (TST), 2021.
Yingdi Wang, Yunzhe Tian, Jiqiang Liu, Wenjia Niu, and Endong Tong. A Training-Based Identification Approach to VIN Adversarial Examples in Path Planning. In Journal of Circuits, Systems and Computers (JCSC), 2021.
Yalun Wu, Minglu Song, Yike Li, Yunzhe Tian, Endong Tong, Wenjia Niu, Bowei Jia, Haixiang Huang, Qiong Li and Jiqiang Liu. Improving Convolutional Neural Network-based Webshell Detection through Reinforcement Learning. In The 23rd International Conference on Information and Communications Security (ICICS 2021), 2021.
Tong Chen, Yingxiao Xiang, Yike Li, Yunzhe Tian, Endong Tong, Wenjia Niu, Jiqiang Liu, Li Gang and Qi Alfred Chen. Protecting Reward Function of Reinforcement Learning via Minimal and Non-catastrophic Adversarial Trajectory. In The 40th International Symposium on Reliable Distributed Systems (SRDS 2021), 2021.
Tong Chen, Jiqiang Liu, Yalun Wu, Yunzhe Tian, Endong Tong, Wenjia Niu, Yike Li, Yingxiao Xiang, Wei Wang. Survey on Astroturfing Detection and Analysis from an Information Technology Perspective. In Security and Communication Networks (SCN), 2021.
王硕汝, 牛温佳, 童恩栋, 陈彤, 李赫, 田蕴哲, 刘吉强, 韩臻, 李浥东. 强化学习离线策略评估研究综述. 计算机学报, 2021.
Xinyu Huang, Yunzhe Tian, Yifei He, Endong Tong, Wenjia Niu, Chenyang Li, Jiqiang Liu, and Liang Chang. Exposing Spoofing Attack on Flocking-based Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Cluster: A Threat to Swarm Intelligence. In Security and Communication Networks (SCN), 2020.
Bowei Jia, Yunzhe Tian, Di Zhao, Xiaojin Wang, Chenyang Li, Wenjia Niu, Endong Tong, and Jiqiang Liu. Bidirectional Rnn-based Few-shot Training for Detecting Multi-stage Attack. In The 16th International Conference on Information Security and Cryptology (INSCRYPT 2020), 2020 .
Qinghua Wen, Yunzhe Tian, Xiaohui Zhang, Ruoyun Hu, Jinsong Wang, Lei Hou, and Juanzi Li. Type-aware Open Information Extraction via Graph Augmentation Model. In China Conference on Knowledge Graph and Semantic Computing (CCKS 2020), 2020 .
Oral Presentation in AUTODRIVING TECH TALK @ BCTF 2022
Oral Presentation in AutoSec Workshop @ NDSS’21
Oral Presentation in Inscrypt 2020, Guangzhou, China
Oral Presentation in ICPADS 2020, Hong Kong, China
Teaching Assistant (Feb. 2023 - Jun. 2023)
M602031B: Situation Awareness of Cyberspace Security
Teaching Assistant (Jun. 2023 - Jul. 2023)
80S504Q: Information Security Professional Practice and Training
Teaching Assistant (Feb. 2024 - Jun. 2024)
M402055B: Artificial Intelligence Security
Research Advising and Mentoring
Team leader for the XAI group, a subgroup within the THETA Lab led by Prof. Wenjia Niu.
-
Sep. 2021 - Jul. 2024, Shiyao Chen (BJTU M.S., now at CMCC)
Awarded Outstanding Master Thesis of Beijing Jiaotong University
-
May. 2022 - Jul. 2024, Zhenglong Liu (BJTU B.S., now M.S. at USC)
Awarded National-level College Student Innovative Training Program
2024, Second Prize in the 34th Huiguang Cup Academic Cultural Festival, Academic Poster Track (coverage: 34th慧光杯 | 优秀学术海报和创新实践竞赛成果展示 )
2023, Fourth Place in IEEE Trojan Removal Competition (IEEE TRC’22), associated with the ICLR’23 workshop.
2023, Excellent Team in DataCon Big Data Security Analysis Competition, AI security Track .
2022, Excellent Graduate of Beijing Jiaotong University
2022, Excellent Master Thesis of Beijing Jiaotong University (coverage: 恭贺田蕴哲同学获优秀硕士学位论文)
2022, First Place in Vulnerability Mining Contest for Olympic Winter Games Beijing (coverage: 计算机学院信安团队参与冬奥卫士演练活动荣获一等奖)
2022, Second Place in DEF CON 30 Contest AutoDriving CTF (coverage: 祝贺计算机学院信息安全系THETA团队在DEFCON30 AutoDriving赛事获得优异成绩)
2021, Second Place in 第二届全国分布式靶场安全技能大赛 (coverage: 信安团队在全国分布式靶场安全技能大赛中勇夺第二名)
2021, Second Place in DEF CON 29 Contest AutoDriving CTF (coverage: DEF CON 29 Contest自动驾驶CTF赛亚军)
2020, Excellent Undergraduate of Beijing
2020, Excellent Undergraduate Thesis of Beijing (coverage: 我校23篇本科生毕业设计(论文)获评北京市优秀毕业设计(论文))
2020, Excellent Undergraduate of Beijing Information Science & Technology University
2020, Excellent Undergraduate Thesis of Beijing Information Science & Technology University
2019, National Scholarship
2019, President Scholarship of Beijing Information Science & Technology University



